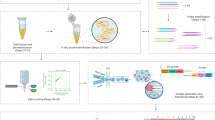
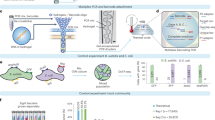
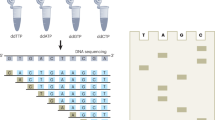
Abstract
Genome sequencing of single cells has a variety of applications, including characterizing difficult-to-culture microorganisms and identifying somatic mutations in single cells from mammalian tissues. A major hurdle in this process is the bias in amplifying the genetic material from a single cell, a procedure known as polymerase cloning. Here we describe the microwell displacement amplification system (MIDAS), a massively parallel polymerase cloning method in which single cells are randomly distributed into hundreds to thousands of nanoliter wells and their genetic material is simultaneously amplified for shotgun sequencing. MIDAS reduces amplification bias because polymerase cloning occurs in physically separated, nanoliter-scale reactors, facilitating the de novo assembly of near-complete microbial genomes from single Escherichia coli cells. In addition, MIDAS allowed us to detect single-copy number changes in primary human adult neurons at 1- to 2-Mb resolution. MIDAS can potentially further the characterization of genomic diversity in many heterogeneous cell populations.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access to this article via ICE Institution of Civil Engineers is not available.
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhang, K. et al. Sequencing genomes from single cells by polymerase cloning. Nat. Biotechnol. 24, 680–686 (2006).
Rodrigue, S. et al. Whole genome amplification and de novo assembly of single bacterial cells. PLoS ONE 4, e6864 (2009).
Fan, H.C., Wang, J., Potanina, A. & Quake, S.R. Whole-genome molecular haplotyping of single cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 51–57 (2011).
Hou, Y. et al. Single-cell exome sequencing and monoclonal evolution of a JAK2-negative myeloproliferative neoplasm. Cell 148, 873–885 (2012).
Pan, X. et al. A procedure for highly specific, sensitive, and unbiased whole-genome amplification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 15499–15504 (2008).
Marcy, Y. et al. Dissecting biological “dark matter” with single-cell genetic analysis of rare and uncultivated TM7 microbes from the human mouth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 11889–11894 (2007).
Yoon, H.S. et al. Single-cell genomics reveals organismal interactions in uncultivated marine protists. Science 332, 714–717 (2011).
Navin, N. et al. Tumour evolution inferred by single-cell sequencing. Nature 472, 90–94 (2011).
Xu, X. et al. Single-cell exome sequencing reveals single-nucleotide mutation characteristics of a kidney tumor. Cell 148, 886–895 (2012).
Wang, J., Fan, H.C., Behr, B. & Quake, S.R. Genome-wide single-cell analysis of recombination activity and de novo mutation rates in human sperm. Cell 150, 402–412 (2012).
Bankevich, A. et al. SPAdes: a new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 19, 455–477 (2012).
Chitsaz, H. et al. Efficient de novo assembly of single-cell bacterial genomes from short-read data sets. Nat. Biotechnol. 29, 915–921 (2011).
Hutchison, C.A. III, Smith, H.O., Pfannkoch, C. & Venter, J.C. Cell-free cloning using phi29 DNA polymerase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 17332–17336 (2005).
Marcy, Y. et al. Nanoliter reactors improve multiple displacement amplification of genomes from single cells. PLoS Genet. 3, 1702–1708 (2007).
Inoue, J., Shigemori, Y. & Mikawa, T. Improvements of rolling circle amplification (RCA) efficiency and accuracy using Thermus thermophilus SSB mutant protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 34, e69 (2006).
Woyke, T. et al. One bacterial cell, one complete genome. PLoS ONE 5, e10314 (2010).
Fitzsimons, M.S. et al. Nearly finished genomes produced using gel microdroplet culturing reveal substantial intraspecies genomic diversity within the human microbiome. Genome Res. 23, 878–888 (2013).
Zong, C., Lu, S., Chapman, A.R. & Xie, X.S. Genome-wide detection of single-nucleotide and copy-number variations of a single human cell. Science 338, 1622–1626 (2012).
Blainey, P.C. & Quake, S.R. Digital MDA for enumeration of total nucleic acid contamination. Nucleic Acids Res. 39, e19 (2011).
Adey, A. & Shendure, J. Ultra-low-input, tagmentation-based whole-genome bisulfite sequencing. Genome Res. 22, 1139–1143 (2012).
Rehen, S.K. et al. Constitutional aneuploidy in the normal human brain. J. Neurosci. 25, 2176–2180 (2005).
Rehen, S.K. et al. Chromosomal variation in neurons of the developing and adult mammalian nervous system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 13361–13366 (2001).
Yang, A.H. et al. Chromosome segregation defects contribute to aneuploidy in normal neural progenitor cells. J. Neurosci. 23, 10454–10462 (2003).
Yurov, Y.B. et al. Aneuploidy and confined chromosomal mosaicism in the developing human brain. PLoS ONE 2, e558 (2007).
Muotri, A.R. & Gage, F.H. Generation of neuronal variability and complexity. Nature 441, 1087–1093 (2006).
Singer, T., McConnell, M.J., Marchetto, M.C., Coufal, N.G. & Gage, F.H. LINE-1 retrotransposons: mediators of somatic variation in neuronal genomes? Trends Neurosci. 33, 345–354 (2010).
Westra, J.W. et al. Neuronal DNA content variation (DCV) with regional and individual differences in the human brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 518, 3981–4000 (2010).
Baslan, T. et al. Genome-wide copy number analysis of single cells. Nat. Protoc. 7, 1024–1041 (2012).
Shendure, J. et al. Accurate multiplex polony sequencing of an evolved bacterial genome. Science 309, 1728–1732 (2005).
Abecasis, G.R. et al. An integrated map of genetic variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature 491, 56–65 (2012).
Albertsen, M. et al. Genome sequences of rare, uncultured bacteria obtained by differential coverage binning of multiple metagenomes. Nat. Biotechnol. 31, 533–538 (2013).
Kirkness, E.F. et al. Sequencing of isolated sperm cells for direct haplotyping of a human genome. Genome Res. 23, 826–832 (2013).
Lu, S. et al. Probing meiotic recombination and aneuploidy of single sperm cells by whole-genome sequencing. Science 338, 1627–1630 (2012).
Hussein, S.M. et al. Copy number variation and selection during reprogramming to pluripotency. Nature 471, 58–62 (2011).
Westra, J.W. et al. Aneuploid mosaicism in the developing and adult cerebellar cortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 507, 1944–1951 (2008).
Huson, D.H., Auch, A.F., Qi, J. & Schuster, S.C. MEGAN analysis of metagenomic data. Genome Res. 17, 377–386 (2007).
Gurevich, A., Saveliev, V., Vyahhi, N. & Tesler, G. QUAST: quality assessment tool for genome assemblies. Bioinformatics 29, 1072–1075 (2013).
Aziz, R.K. et al. The RAST Server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics 9, 75 (2008).
Moriya, Y., Itoh, M., Okuda, S., Yoshizawa, A.C. & Kanehisa, M. KAAS: an automatic genome annotation and pathway reconstruction server. Nucleic Acids Res. 35, W182–W185 (2007).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Chen, H. Choi and the UCSD Nano3 facility for initial help with microwell fabrication, F. Liang for initial technical assistance and P. Pevzner for advice on de novo genome assembly. This project was funded by US National Institutes of Health grants R01HG004876, R01GM097253, U01MH098977 and P50HG005550, and National Science Foundation grant OCE-1046368.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.G. and K.Z. conceived and designed the experiments. J.G., A.R. and H.-I.C. performed the experiments. J.G. and Y.-J.C. fabricated the microwell arrays. H.-L.F. performed sequencing. D.B. provided neuronal nuclei. J.G., A.G. and K.Z. analyzed data and wrote the manuscript with input from Y.-H.L. and J.C.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
J.G. and K.Z. are listed as co-inventors in a patent application related to this work.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–9 and Supplementary Tables 1–8 (PDF 8627 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gole, J., Gore, A., Richards, A. et al. Massively parallel polymerase cloning and genome sequencing of single cells using nanoliter microwells. Nat Biotechnol 31, 1126–1132 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2720
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.2720