Summary
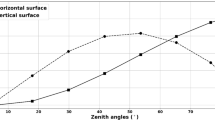
The increases in the erythemal UV exposures to horizontal planes and to inclined planes over three surfaces that are found in an urban environment (water, concrete and sand) due to the albedo of these surfaces have been estimated. For the cloud free case, the additional daily estimated UV exposures to a horizontal plane have a maximum value of 222 (J m−2)ER, where the index after the unit is there to indicate that it refers to a biologically effective exposure. In comparison, the daily erythemal UV exposures over a year to a horizontal plane ranged from 425 to 8,321 (J m−2)ER. For a vertical receiving plane that is rotating about a vertical axis, the additional erythemal daily UV exposures for the sub-tropical latitude ___location of this research for the ranges of solar azimuth angles encountered over the days in each season ranged from 16 to 311 (J m−2)ER, 29 to 566 (J m−2)ER and 46 to 905 (J m−2)ER for water, concrete and sand respectively. The estimated error is ±20% and the calculations are based on clear-sky conditions. The additional erythemal UV averaged over each of the seasons was higher for the receiving plane inclined at 45° below the horizontal plane. In a similar fashion, the vertical surface has the higher additional erythemal UV exposures compared to the surfaces inclined at an angle above the horizontal.
Article PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parisi, A., Sabburg, J., Kimlin, M. et al. Measured and modelled contributions to UV exposures by the albedo of surfaces in an urban environment. Theor Appl Climatol 76, 181–188 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-003-0012-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-003-0012-9