Ddsasasad
Uploaded by
Evubha GooDungarDdsasasad
Uploaded by
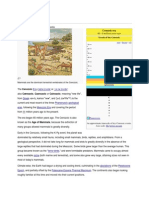
Evubha GooDungarThe Cretaceous ( /krɪˈteɪʃəs/, kri-TAY-shəs) is a geologic period and system that spans from the
end of the Jurassic Period 145 million years ago (mya) to the beginning of the Paleogene Period
66 mya. It is the last period of the Mesozoic Era, and the longest period of the Phanerozoic Eon.
The Cretaceous Period is usually abbreviated K, for its German translation Kreide (chalk, creta in
Latin).
The Cretaceous was a period with a relatively warm climate, resulting in high eustatic sea
levels that created numerous shallow inland seas. These oceans and seas were populated with
now-extinct marine reptiles, ammonites and rudists, while dinosaurs continued to dominate on
land. During this time, new groups of mammals and birds, as well as flowering plants, appeared.
The Cretaceous (along with the Mesozoic) ended with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction
event, a large mass extinction in which many groups, including non-avian
dinosaurs, pterosaurs and large marine reptiles died out. The end of the Cretaceous is defined
by the abrupt Cretaceous–Paleogene boundary (K–Pg boundary), a geologic signature
associated with the mass extinction which lies between the Mesozoic and Cenozoic eras.
You might also like
- Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, and PermianNo ratings yetCambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, and Permian5 pages
- Geologic Time: Geologic Time Scale Relative Dating Principles Absolute Dating W/ Radioactivity Correlation of Rock LayersNo ratings yetGeologic Time: Geologic Time Scale Relative Dating Principles Absolute Dating W/ Radioactivity Correlation of Rock Layers53 pages
- Mesozoic ERA: Plateosaurus (A Prosauropod)No ratings yetMesozoic ERA: Plateosaurus (A Prosauropod)2 pages
- Periods of The Paleozoic Era: Cambrian PeriodNo ratings yetPeriods of The Paleozoic Era: Cambrian Period8 pages
- Cenozoic Era:: The Cenozoic Meaning "New Life" This Era Includes Last 65 Millions Years of Earth HistoryNo ratings yetCenozoic Era:: The Cenozoic Meaning "New Life" This Era Includes Last 65 Millions Years of Earth History54 pages
- Mass Extinctions: Fossil Cretaceous Period Triassic Period Permian Period Devonian Period Ordovician PeriodNo ratings yetMass Extinctions: Fossil Cretaceous Period Triassic Period Permian Period Devonian Period Ordovician Period2 pages
- Mesozoic Era and How It Is Begun JonelleNo ratings yetMesozoic Era and How It Is Begun Jonelle4 pages
- Geologic Time Scale: Cambrian Ordovician Silurian Devonian Carboniferous PermianNo ratings yetGeologic Time Scale: Cambrian Ordovician Silurian Devonian Carboniferous Permian2 pages
- Boundaries: International Commission On Stratigraphy Cretaceous-Paleogene BoundaryNo ratings yetBoundaries: International Commission On Stratigraphy Cretaceous-Paleogene Boundary4 pages
- Genbio2 Lesson 2 Origin of Life and Diversity Part 1No ratings yetGenbio2 Lesson 2 Origin of Life and Diversity Part 126 pages
- Cenozoic: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaNo ratings yetCenozoic: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia3 pages
- See Results About: Britney Spears - 3 (Official Music Video) - YoutubeNo ratings yetSee Results About: Britney Spears - 3 (Official Music Video) - Youtube3 pages
- Dungeons &: Do Not Disturb Registration Online - DND Activation - NDNC ..No ratings yetDungeons &: Do Not Disturb Registration Online - DND Activation - NDNC ..2 pages
- Watch: Shopping Books Images Maps More Settings ToolsNo ratings yetWatch: Shopping Books Images Maps More Settings Tools2 pages
- Tinashe - 2 On (Explicit) Ft. Schoolboy Q - Youtube: LyricsNo ratings yetTinashe - 2 On (Explicit) Ft. Schoolboy Q - Youtube: Lyrics3 pages
- Search Google or Type A URL: Gmail ImagesNo ratings yetSearch Google or Type A URL: Gmail Images1 page
- Create Harvard, APA & MLA Citations For Your Bibliography: Cite Smarter, Worry Less With Cite This For Me PremiumNo ratings yetCreate Harvard, APA & MLA Citations For Your Bibliography: Cite Smarter, Worry Less With Cite This For Me Premium2 pages
- Showing Results For: Essential Elements of StateNo ratings yetShowing Results For: Essential Elements of State2 pages
- Citation Machine - Format & Generate Citations - APA, MLA, & ChicagoNo ratings yetCitation Machine - Format & Generate Citations - APA, MLA, & Chicago3 pages
- Shreya Matilal Assistant Professor of Law - Google SearchNo ratings yetShreya Matilal Assistant Professor of Law - Google Search5 pages
- Search Google or Type A URL: Gmail ImagesNo ratings yetSearch Google or Type A URL: Gmail Images1 page
- Health Department Victoria .General Pathology Training PositionNo ratings yetHealth Department Victoria .General Pathology Training Position1 page
- Price Fixing Restrictive Practices Antitrust Monopoly Oligopolies Homogeneous ProductsNo ratings yetPrice Fixing Restrictive Practices Antitrust Monopoly Oligopolies Homogeneous Products3 pages