What is IT asset management (ITAM)?
IT asset management (ITAM) is a set of business practices that combines financial, inventory and contractual functions to optimize spending and support lifecycle management and strategic decision-making within the IT environment. ITAM is often a subset of the IT service management (ITSM) process.
An IT asset is classified as any company-owned information, system or hardware used in business activities. The IT asset management process typically involves performing asset discovery and gathering a detailed inventory of an organization's hardware, software and network assets and then making informed business decisions about IT-related purchases and redistribution.
ITAM applications are available to organizations to assist in the ITAM process. These applications can detect the hardware, software and network assets across an organization and then capture, record and make the data available. Some of these applications integrate ITAM with the service desk, keeping user and access information together with incidents and requests.
Why ITAM is important
ITAM is about more than creating an asset inventory. It's about continually using the captured asset data to maximize returns, minimize risk and drive increased business value of the IT infrastructure. By avoiding unnecessary asset purchases and making the best use of current resources, IT asset managers can cut software licensing and support costs, manage warranty issues, identify potential asset vulnerabilities, eliminate waste and improve efficiency.
This article is part of
What is desktop management and how does it work?
ITAM also helps increase the companywide understanding of IT's business value, improves communications and understanding between IT and other departments, supports efficient workflows, enforces compliance with cybersecurity policies and regulatory requirements, improves productivity through technical support and limits overhead costs of managing the IT environment.
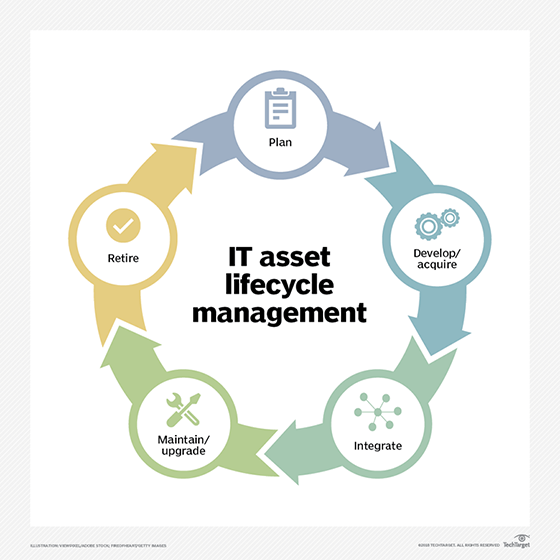
What are the types of IT asset management?
The four primary types of ITAM implementations are the following:
- Hardware and software asset management. In this type of strategy, IT has an asset inventory management platform that focuses solely on delivering IT hardware asset management, addressing endpoint devices, e.g., laptops; mobile devices; servers; workstations; and any software in use.
- Cloud asset management. A cloud asset management tool focuses on supporting the management of cloud asset services from Amazon, Microsoft, Google or other cloud service providers.
- Digital asset management. Digital asset management tools are mainly used by organizations that manage digital content to track licensing, formats, metadata and other attributes. These tools provide features and functionality not found in other products.
- Fixed asset management. These tools track assets, including desks, printers, networking cabinets, server room air conditioning units and any other fixed IT assets within the environment.
Benefits of IT asset management
There are numerous benefits of having an IT asset management process in place, including the following:
- Maintaining a centralized ___location for all asset information for IT.
- Eliminating unused or unnecessary assets to realize cost savings.
- Having better visibility into where assets are and detailed information related to them.
- Ensuring license compliance to prevent any unanticipated issues.
- Reducing security risks by keeping track of all assets and ensuring that updates and patches are applied.
- Ensuring that IT asset disposal is consistent with IT requirements.
- Staying organized with all the different asset categories and reporting on them.
- Ensuring environmental protection by eliminating waste through duplicate purchases of assets.
Downsides of IT asset management
Establishing an IT asset management program can be expensive, especially relating to IT asset management software and potential employee training. The implementation process can be complex and time-consuming, especially for system administration, employee training and system maintenance. Ensuring that asset data collected is accurate can be difficult, and integration with existing systems and processes may also present technical challenges.
Asset management vs. configuration management
Asset management (AM) and configuration management (CM) are sometimes used interchangeably; however, they are separate yet complementary activities. Think of asset management as the "what" in an IT organization and configuration management as "how" the various assets operate, either individually or in concert with other systems.
AM discovers, collects and organizes asset data for user review and analysis. By contrast, CM captures data on how each asset is used, how it operates and how it should be programmed or configured for proper operation. Just as assets are assembled into a database, so too are configuration details assembled into a CM database.
ITAM best practices
The successful implementation of ITAM results from proper planning and a few other considerations, including the following:
- Determining what type of tool addresses the current needs for asset management.
- Establishing a policy for IT asset management.
- Defining standard operating procedures for asset tracking, documentation in the system and how to use the system.
- Creating a consistent tracking method to ensure that all relevant assets are accounted for.
- Performing frequent audits of asset management by reviewing and updating existing assets based on a schedule.
- Having the ability to track critical data, such as expiration dates, purchase dates, license and warranty data, vendor contact information and other relevant details.
ITAM software tools
There are many ITAM options, both on-site enterprise-ready and cloud-based, e.g., software as a service, including the following:
- Asset Panda.
- Freshservice.
- GoCodes.
- Ivanti IT Asset Management Suite.
- ManageEngine AssetExplorer.
- ServiceNow.
- SysAid.
Effectively managing IT assets can also improve visibility and control of IT assets and help swiftly identify and replace stolen hardware and software components.
ITAM can provide accurate information about the assets affected by an incident, problem or change. ITAM also makes organizations more nimble by enabling quicker and more accurate migrations, upgrades and companywide changes.
IT asset and configuration data can be critical in the aftermath of natural disasters and other unexpected events. Proper ITAM can help leaders quickly identify the effects of such events and more confidently make decisions to restore services.
IT asset management processes
ITAM is a continual and systematic process, so the asset lifecycle concept helps structure activities and support decision-making. The cycle starts with strategic planning across the organization to determine what assets are needed, how to procure them, how to establish licensing agreements and other arrangements, the specific ways the assets will be used and how their purchases will be funded. This often includes total cost of ownership estimates and a cost-benefit analysis of alternatives.
Next is the procurement phase, in which organizations build, purchase, lease or license the assets they need. The integration phase follows, during which the assets are installed and introduced into the digital ecosystem. This includes properly integrating the assets with other components, establishing support and operations processes, and specifying user access.
Maintaining and upgrading the assets is the next phase of the IT asset lifecycle. To maximize the value of the asset and extend its life -- as well as mitigate risks and reduce support costs -- maintenance, repair and extensive overhauls may be necessary.
Once the asset has reached the end of its useful life, the last phase is asset retirement and disposal. That often includes "transitioning users to other resources, updating asset records, canceling support agreements, license management activities including renewing and terminating licenses, and initiating the planning for replacement assets," according to Freshservice, a cloud-based service desk and ITSM system. An ITAM system can help ensure license compliance.
ISO standards for ITAM
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has established an official set of standards for ITAM. This family of standards, ISO/International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) 19770, Information technology -- IT asset management, consists of five major parts and was most recently updated in 2017. The five parts entail the following, as described by Freshservice:
- ISO/IEC 19770-1 -- Requirements. This part is a process framework that outlines best practices for ITAM in an organization. It provides organizations a way to prove that they're performing ITAM per the standards that satisfy corporate governance requirements and support ITSM activities.
- ISO/IEC 19770-2 -- Software identification tag. This is a data standard for software identification tags that enables organizations to identify software deployed on a given device.
- ISO/IEC 19770-3 -- Entitlement schema. This is a data standard for providing details of the entitlements and rights associated with a piece of software and the method for measuring license or entitlement consumption.
- ISO/IEC 19770-4 -- Resource utilization measurement. The fourth part is a measurement standard that enables standardized reporting of resource utilization. This standard is especially important when managing complex data center licenses and cloud-based software and hardware.
- ISO/IEC 19770-5 -- Overview and vocabulary. Part five provides an overview of the ISO-defined ITAM standards and associated vocabulary.
Additional asset management standards
- ISO 55001:2024 Asset management -- Asset management system -- Requirements. This standard addresses all kinds of physical assets, not just IT, and provides a framework for managing assets throughout their lifecycle.
- NIST Special Publication 1800-5. Released in 2018, this National Institute for Standards and Technology publication was designed primarily for financial service organizations and provides guidance on implementing an effective ITAM process. Its guidance can also be applied to public and private institutions.
- ITIL Service Asset and Configuration Management. Part of the Information Technology Infrastructure Library Service Transition stage, this program provides guidance on all aspects of IT asset and lifecycle management.
Preparing an IT asset management policy
Assuming IT asset management is an established activity, it makes good sense to establish a formal policy. The following items should be included in such a policy:
- Purpose and scope. Establishes what the policy addresses and assets to be managed.
- Roles and responsibilities. Defines who is responsible for IT asset management activities.
- Asset inventory management. Defines how inventories are assembled, organized, classified and managed.
- Asset procurement. Establishes a procurement plan that defines the steps to take to acquire an IT asset.
- Asset tracking. Establishes how IT assets are monitored and tracked throughout their lifecycles.
- Asset lifecycle management. Defines how assets are addressed at every stage of the asset lifecycle.
- Software asset management. Addresses software acquisition, licensing and other activities.
- Security. Ensures that assets are protected from unauthorized access and use.
- Compliance. Establishes guidelines for ensuring that asset management processes comply with relevant standards.
- Maintenance and support. Defines how IT assets are to be maintained and supported through their lifecycles.
- Decommissioning and disposal. Establishes procedures for environmentally friendly disposal and decommissioning of IT assets.
- Auditing and reporting. Ensures that data on IT assets is reported as required and that the asset management process is prepared for potential audits.
- Awareness and training. Provides guidance to employees on the ITAM policy and training to employees who are involved in ITAM activities.
- Review and update. Establishes a process and schedule for periodically reviewing the policy and updating it as needed.
The impact of AI on IT asset management
IT asset management systems that use AI provide greater performance and reduce costs by automating asset and inventory management functions, allow the use of a variety of data analytics for predictive maintenance, deliver better security to prevent unauthorized access and cyberattacks, ensure compliance with relevant standards and regulations, and protect the environment through equipment reuse and proper disposal.
Asset-intensive organizations gain significant advantages from enterprise asset management software, as it enhances the support for their industrial infrastructure. See how enterprise asset management software simplifies that process.
Emily McLaughlin previously contributed to this definition.






